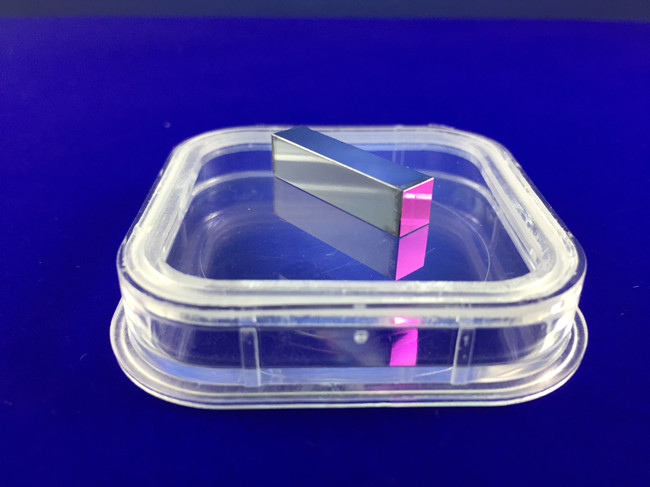



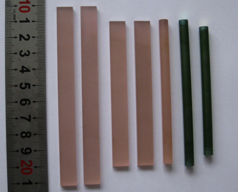
ZnGeP2 Nonlinear Crystals
-
Payment


-
Origin
China Mainland
-
Minimum Order
1
-
Packing
Pieces
- Contact Now Start Order
- Description
Product Detail
Wide transmission region from 0.74 um to 12um
Large nonlinear coefficient
Good mechanical and physical properties
Relatively high damage threshold
Phase matchable over a broad spectral region
High thermal conductivity
Second, third, and fourth harmonic generation of CO2 laser
Optical parametric generation (OPO) with pumping at a wavelengths of 2.05-2.94 µm and possibility to generate effectively 3-10 µm ranges
Second harmonic generation of CO-laser
Producing coherent radiation in sub-millimeter-range from 70.0 µm to 1000 µm - terahertz range
Generation of combined frequencies of CO2- and CO-lasers radiation and other lasers are working in the crystal transparency region
Description
Zinc germanium phosphide (ZnGeP2) is an excellent mid-IR nonlinear crystal with many outstanding fundamental properties. ZnGeP2 (ZGP) crystal has large nonlinear susceptibility (d36~75 pm/V), which is approximately 160 times that of KDP. ZGP exhibits good optical transparency over the 0.74–12 um wavelength region and relatively high laser damage threshold, and is therefore well suited for producing tunable laser output in the near infrared. ZGP is a very promising material for applications such as SHG, SFG, OPO, and OPG/OPA in the mid-infrared region.
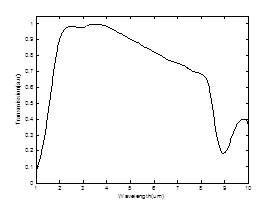
Note: The Transmission spectra of 15 mm long AR coated ZnGeP2 crystal
Features
Applications
Chemical and Physical Properties
Property | Value |
Chemical formula | ZnGeP2 |
Crystal structure | Tetragonal,`42m |
Lattice Parameter | a=b=5.467Å, c=12.736Å |
Mass density | 4.16 g/cm3 |
Moh hardness | 5.5 |
Melting point | About 1040°C |
Thermal conductivity | 180 W/m/K |
Thermal expansion coefficient | ß?,5x10-6/K; ß?,7.8x10-6/K |
Birefringence | positive uniaxial |
Linear Optical Properties
Property | Value |
Transparency Range | 0.74 - 12 um |
Absorption Coefficient: | a<0.05cm-1 @2050-2100 nm |
Refractive Indices @ 2.05 um @ 2.79 um @ 5.30 um @ 10.6 um |
no = 3.1478, ne = 3.1891 no = 3.1333, ne = 3.1744 no = 3.1136, ne = 3.1547 no = 3.0729, ne = 3.1143 |
Sellmeier Equations(? in µm) | no2(?) = 4.64467+5.10087/(?2-0.13656)+4.27777?2/(?2-1653.89) ne2(?) = 4.71539+5.26358/(?2-0.14386)+2.37310?2/(?2-1000.82) |
Nonlinear Optical Properties
Property | Value |
SHG Phase Matchable Range | 3177 ~ 10357nm (Type I) |
NLO coefficients | d36=75 ± 8 pm/V Type ? deeo=d36 sin2?cos2f Type ? doeo=deoo=d36 sin?sin2f |
Damage Threshold at 2.79 um at 10.6 um |
30 GW/cm2 (150 ps) 1 GW/cm2 (2 ns) |

Figure 2. OPO tuning curves of ZGP with pump light of 2090 nm

Figure 3. OPO tuning curves of ZGP with pump light of 2800 nm

Figure 4. SHG curves of ZGP (TypeI (eeo))
Polishing Specification
Property | Value |
Orientation Tolerence | < 0.5° |
Thickness/Diameter Tolerance | ±0.05 mm |
Surface Flatness | <?/8@632 nm |
Wavefront Distortion | <?/4@632 nm |
Surface Quality | 10/5 |
Parallel | 30? |
Perpendicular | 15´ |
Clear Aperture | >90% |
Chamfer | <0.2×45° |
Standard products
Crystal dimension/mm | Application | Orientation Theta/Phi deg | Coatings |
7x5x15 | OPO @ 2.1-> 3.5-5 µm | 54/0 | AR@2.1µm+BBAR@3.5-5µm |
7x5x20 | OPO @ 2.1-> 3.5-5 µm | 54/0 | AR@2.1µm+BBAR@3.5-5µm |
7x5x25 | OPO @ 2.1-> 3.5-5 µm | 54/0 | AR@2.1µm+BBAR@3.5-5µm |
Q&A
Q: What is phase mismatching?
A: A group of techniques for achieving efficient nonlinear interactions in a medium. Many phase-sensitive nonlinear processes, in particular parametric processes such as frequency doubling, sum and difference frequency generation, parametric amplification and oscillation, and also four-wave mixing, require phase matching to be efficient. Essentially, this means ensuring that a proper phase relationship between the interacting waves (for optimum nonlinear frequency conversion) is maintained along the propagation direction. Only if that condition is fulfilled, amplitude contributions from different locations to the product wave are all in phase at the end of the nonlinear crystal.
Q: What is Second harmonic generation (SHG)?
A: SHG is a nonlinear optical process, in which photons with the same frequency interacting with a nonlinear material are effectively "combined" to generate new photons with twice the energy, and therefore twice the frequency and half the wavelength of the initial photons.
- GGG Laser Crystals 1 Pieces / (Min. Order)
- GSGG Laser Crystals 1 Pieces / (Min. Order)
- YAP Laser Crystals 1 Pieces / (Min. Order)
- YAG Laser Crystals 1 Pieces / (Min. Order)
- Er Glass 1 Pieces / (Min. Order)
- Diffusion Bonding Crystals 1 Pieces / (Min. Order)
- Co Spinel Q Switch Crystals 1 Pieces / (Min. Order)
- Cr YAG Q Switch Crystals 1 Pieces / (Min. Order)





 Favorites
Favorites
